Pulmonary artery
| Artery: Pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
| Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. (Pulmonary artery labeled at upper right.) | |
 |
|
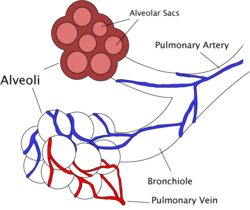
| Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
| Latin | truncus pulmonalis, arteria pulmonalis |
| Gray's | subject #141 543 |
| Source | right ventricle |
| Vein | pulmonary vein |
| Precursor | truncus arteriosus |
| MeSH | Pulmonary+Artery |
The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries (other than umbilical arteries in the fetus) that carry deoxygenated blood.
In the human heart, the pulmonary trunk (pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery) begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short and wide - approximately 5 cm (2 inches) in length and 3 cm (1.2 inches) in diameter. It then branches into two pulmonary arteries (left and right), which deliver de-oxygenated blood to the corresponding lung.
Contents |
Role in disease
Pulmonary hypertension occurs alone and as a consequence of a number of lung diseases. It can also be a consequence of heart disease (Eisenmenger's syndrome) but equally a cause (right-ventricular heart failure); it also occurs as a consequence of pulmonary embolism and scleroderma. It is characterised by reduced exercise tolerance. Severe forms, generally, have a dismal prognosis.
Additional images
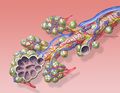 Bronchial anatomy |
 Bronchi, bronchial tree, and lungs |
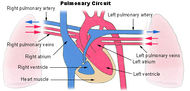 Pulmonary circuit |
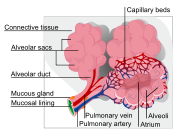 Alveolus diagram |
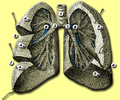 Anatomy of lungs. |
 Front view of heart and lungs. |
 Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery. |
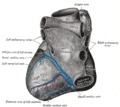 Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart. |
 The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind. |
See also
- Chronic obstructive lung disease
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Thromboembolic disease
- Pulmonary circulation
- Rasmussen's aneurysm
External links
- 53805116 at GPnotebook
- pulmonary+trunk at eMedicine Dictionary
- SUNY Labs 20:01-0106 - "Heart: The Pericardial sac and Great vessels"
- SUNY Labs 20:07-0105 - "Heart: Openings of Great Vessels into the Pericardial Sac"
- SUNY Figs 19:05-06 - "Mediastinal surface of the right lung."
- SUNY Figs 19:06-02 - "Mediastinal surface of the left lung."
- Histology at BU 13802loa
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||